Trivia: What is the closest star to the Earth?
Answer: The Sun
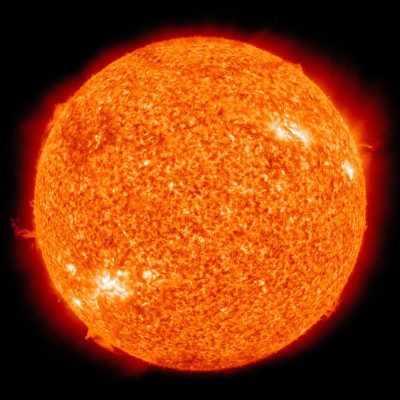

The Sun is a star located within the Milky Way galaxy, and it’s the center of this solar system. However, the true nature of a star can be observed from space using a telescope because much of its body cannot be seen from the Earth’s surface due to its size. That being said, astronomers have observed several other stars and planets within this galaxy that also appear to be close to Earth, but each of these objects has not been proved to exist.
The sun’s distance to the Earth is about 149,600,000 kilometers or 92,960,000 miles. The sun is approximately 1,392,000 kilometers (865,888 miles) in diameter which means that the Earth can fit into it 10 billion times.
The sun has an estimated weight of 2 nonillions (a number with 30 zeros) kilograms and a mass of 2.0991×10^30 kilograms (330,000 times the mass of Earth). One ton is equivalent to about 1,000 kilograms, and 2 nonillion tons is like putting 20 million billion tons into a large box.
In layman’s terms, the distance is so great that it would take a plane traveling at the speed of light more than 8 minutes to reach the sun from Earth.
The closest star to Earth is Proxima Centauri, which is about 4.24 light-years or 24 trillion kilometers away, and it’s part of the Alpha Centauri system. The second closest star system to us is Alpha Centauri, which includes a binary pair and Proxima Centauri. The stars in this system are about 4.367 light-years from the Earth.
The sun emits types of radiation such as X-rays, ultraviolet radiation, microwaves, infrared waves, and radio waves. The sun is also composed of hydrogen, helium, and iron.
Before the 1800s, scientists believed that there were 7 planets in this solar system because they saw 6 objects when observing the sky. Uranus was discovered in 1781, followed by Neptune in 1846 and then Pluto in 1930.
They were named “planets” until 2006 when the International Astronomical Union (IAU) created a new definition of a planet that excluded Pluto. Today, 8 objects orbit around the sun, and each is named after a Greek or Roman god.


